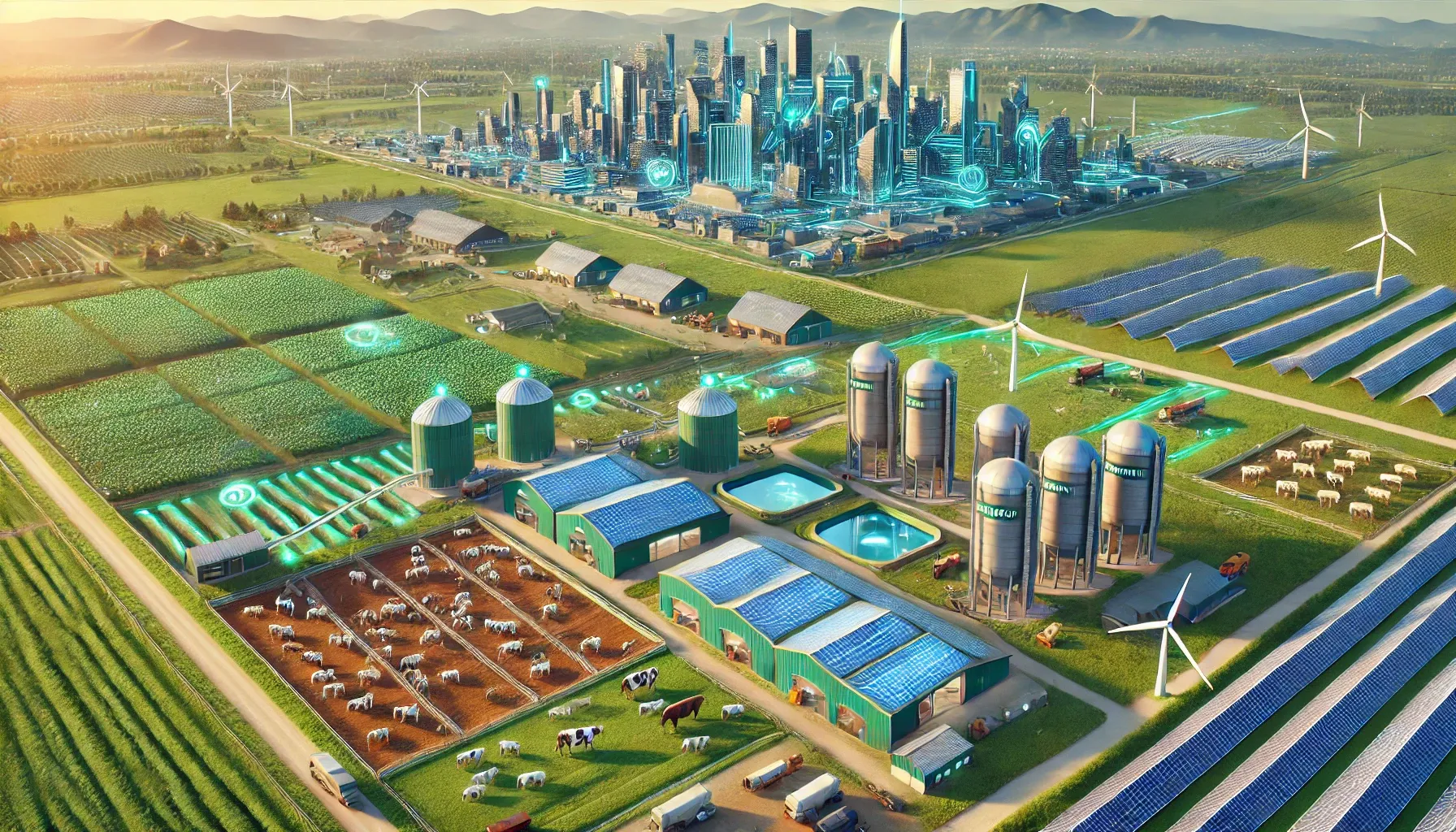
Agriculture and Livestock concept
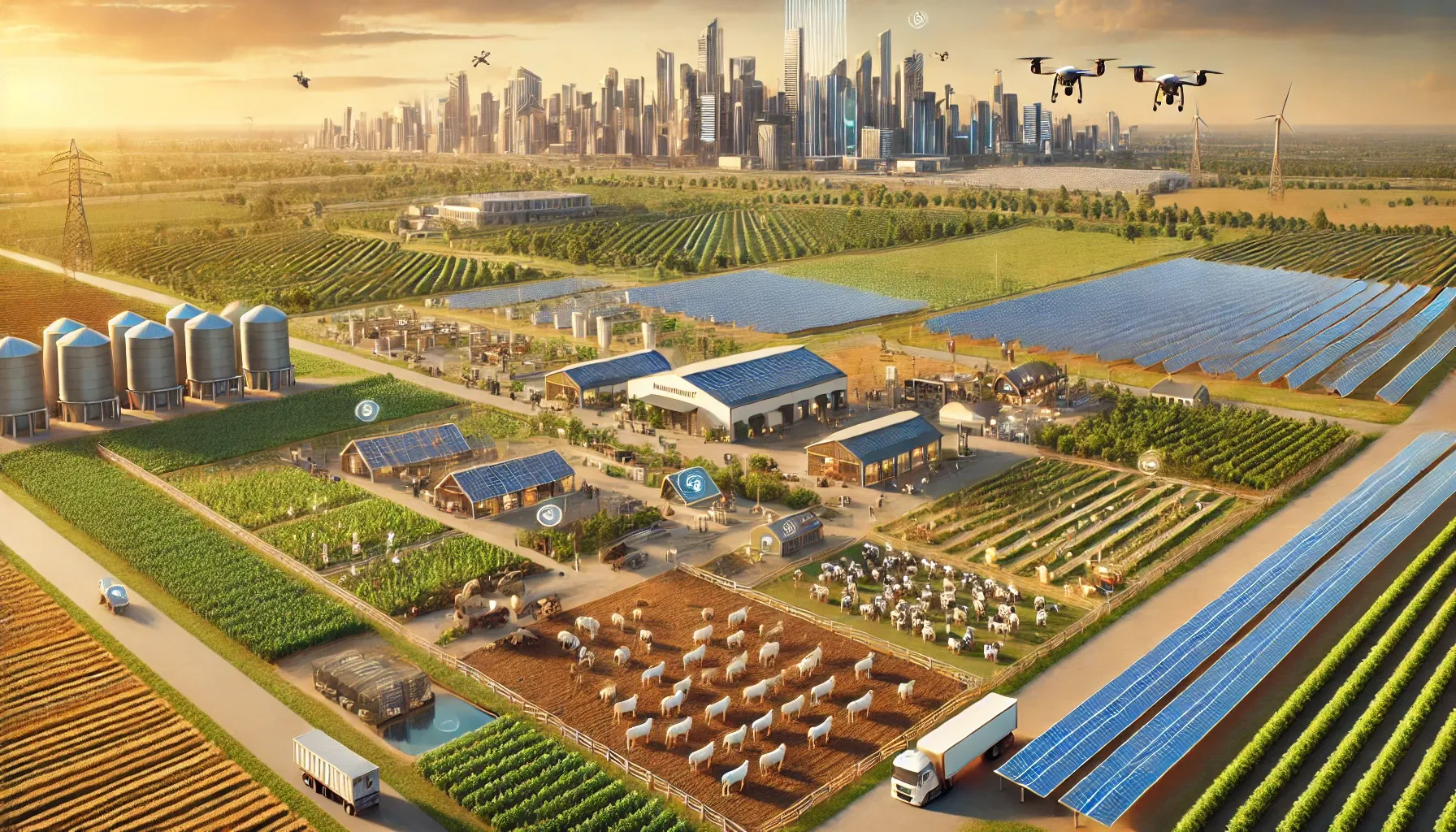
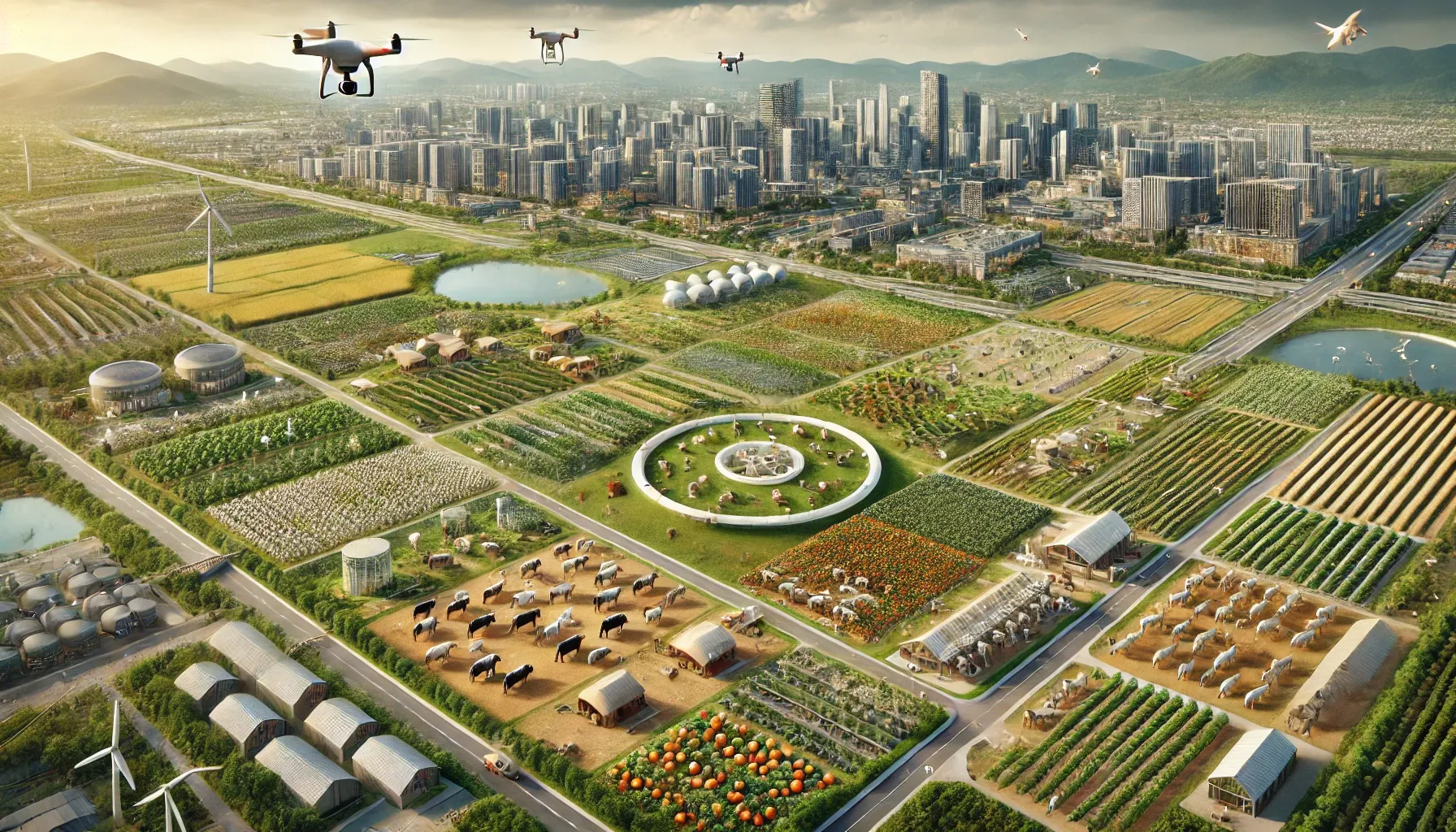
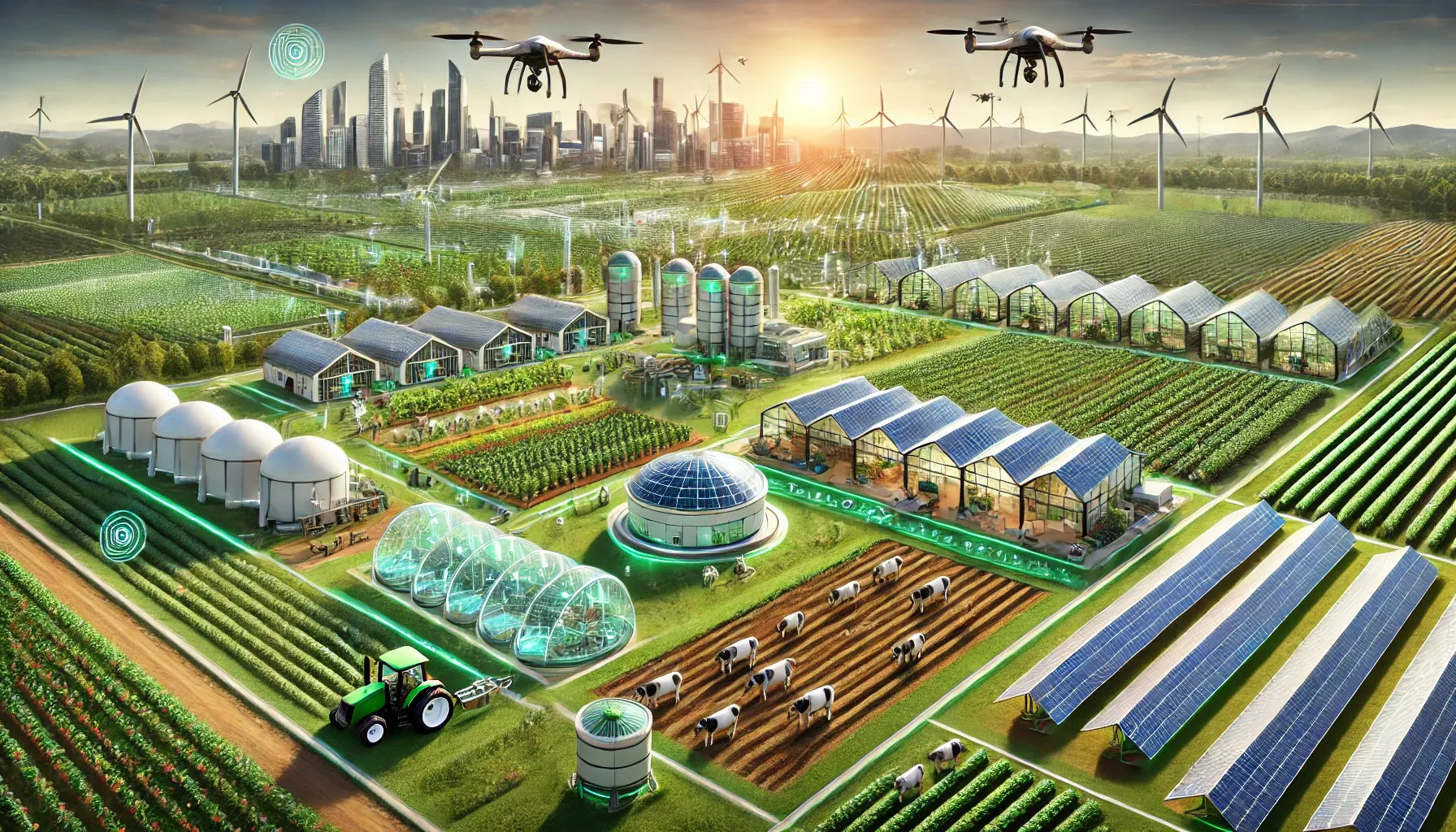
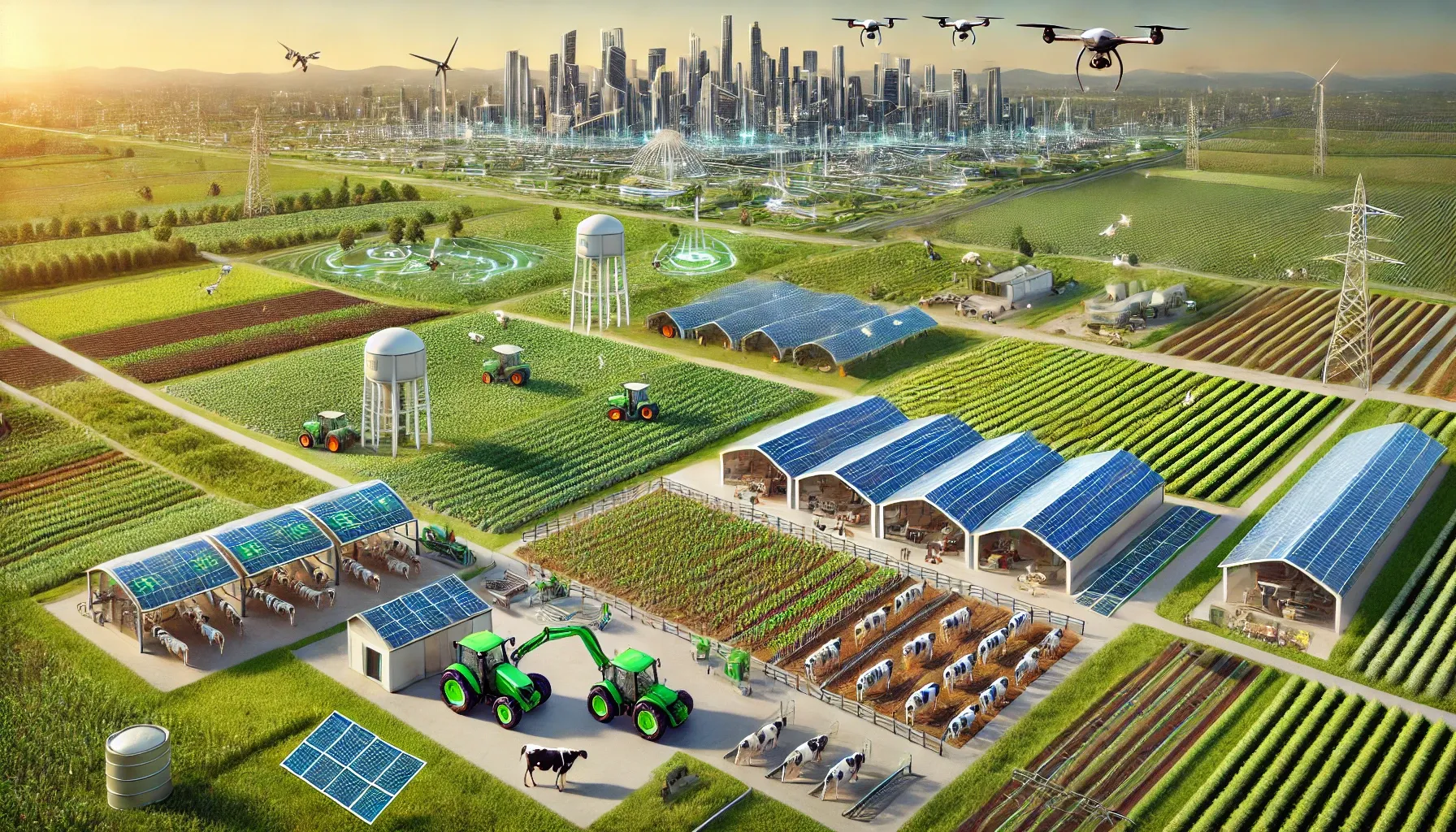
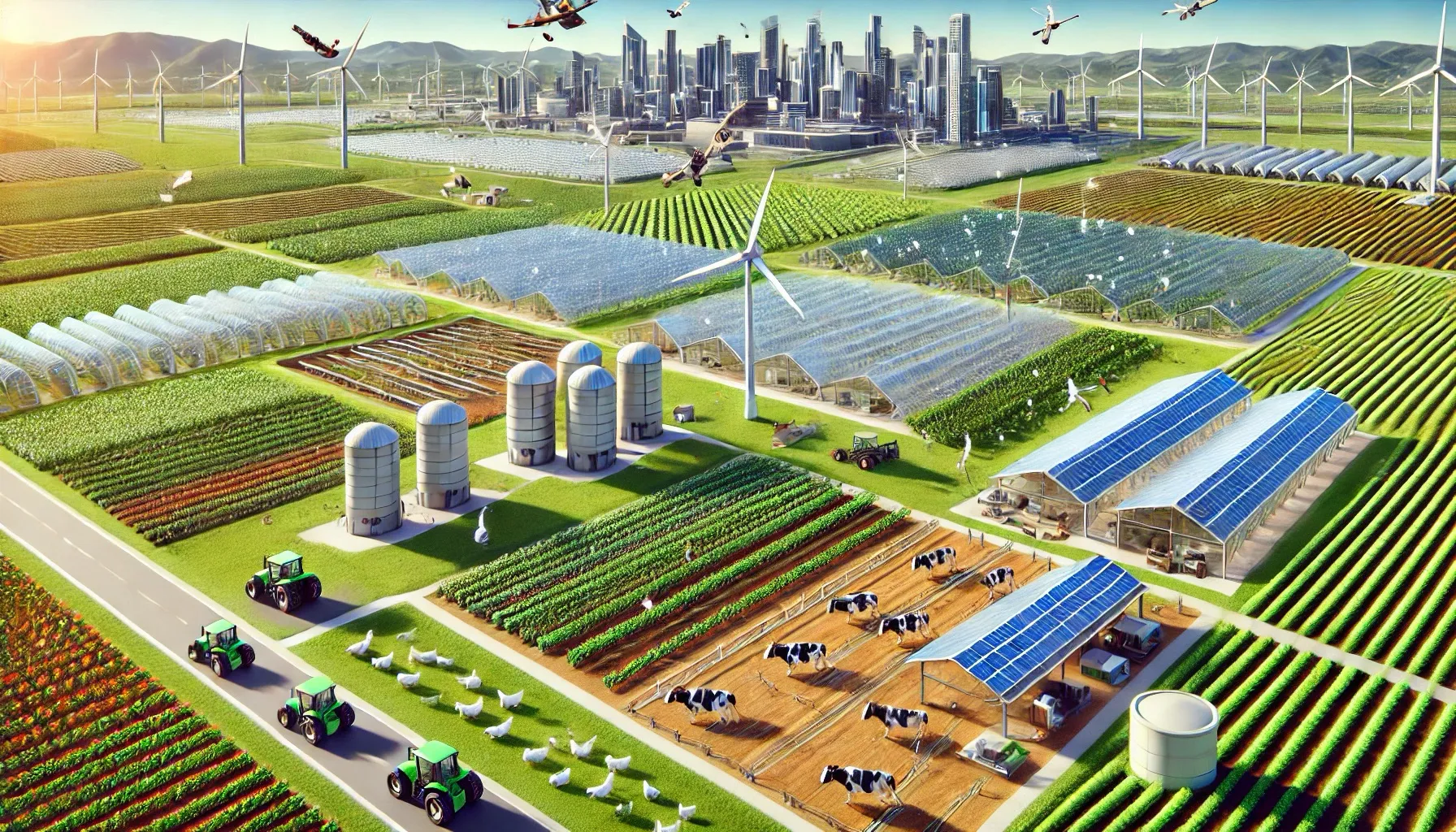
The AHNAKOT Agriculture and Livestock concept on 40,000 hectares near AHNAKOT SMART CITY will integrate modern and sustainable agricultural practices, ensuring synergy between agriculture and urban development. Here are some key elements that will be included in this concept
- Visits: Different zones for rice, fruits and vegetables, designed for local consumption and export.
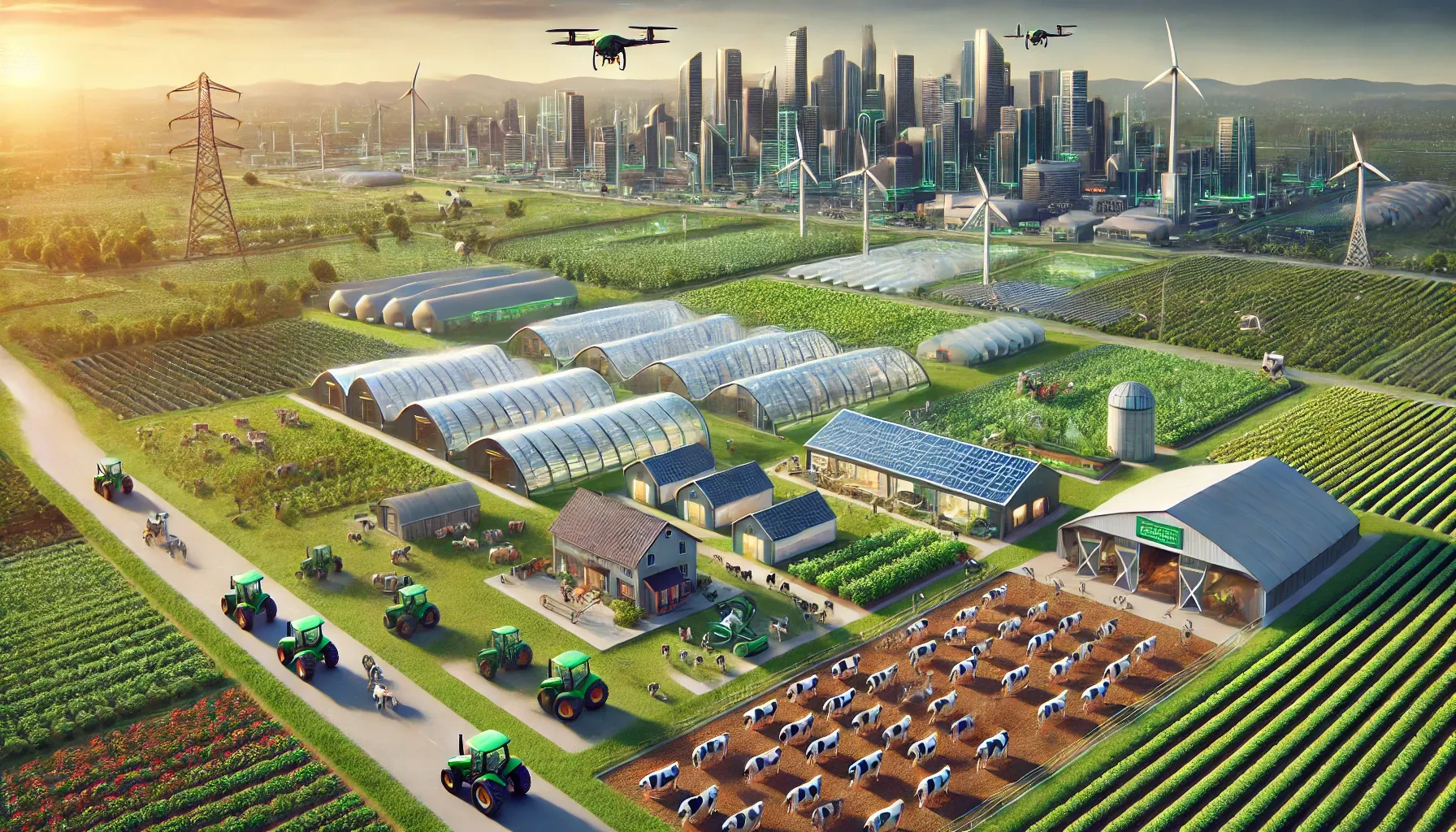
- Livestock: Dedicated areas for raising cattle, poultry and goats, with sustainable grazingpractices.
- Aquaculture: Ponds and irrigation tanks, which provide an additional source of food.
- Agroforestry: Combined agriculture with trees to promote biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
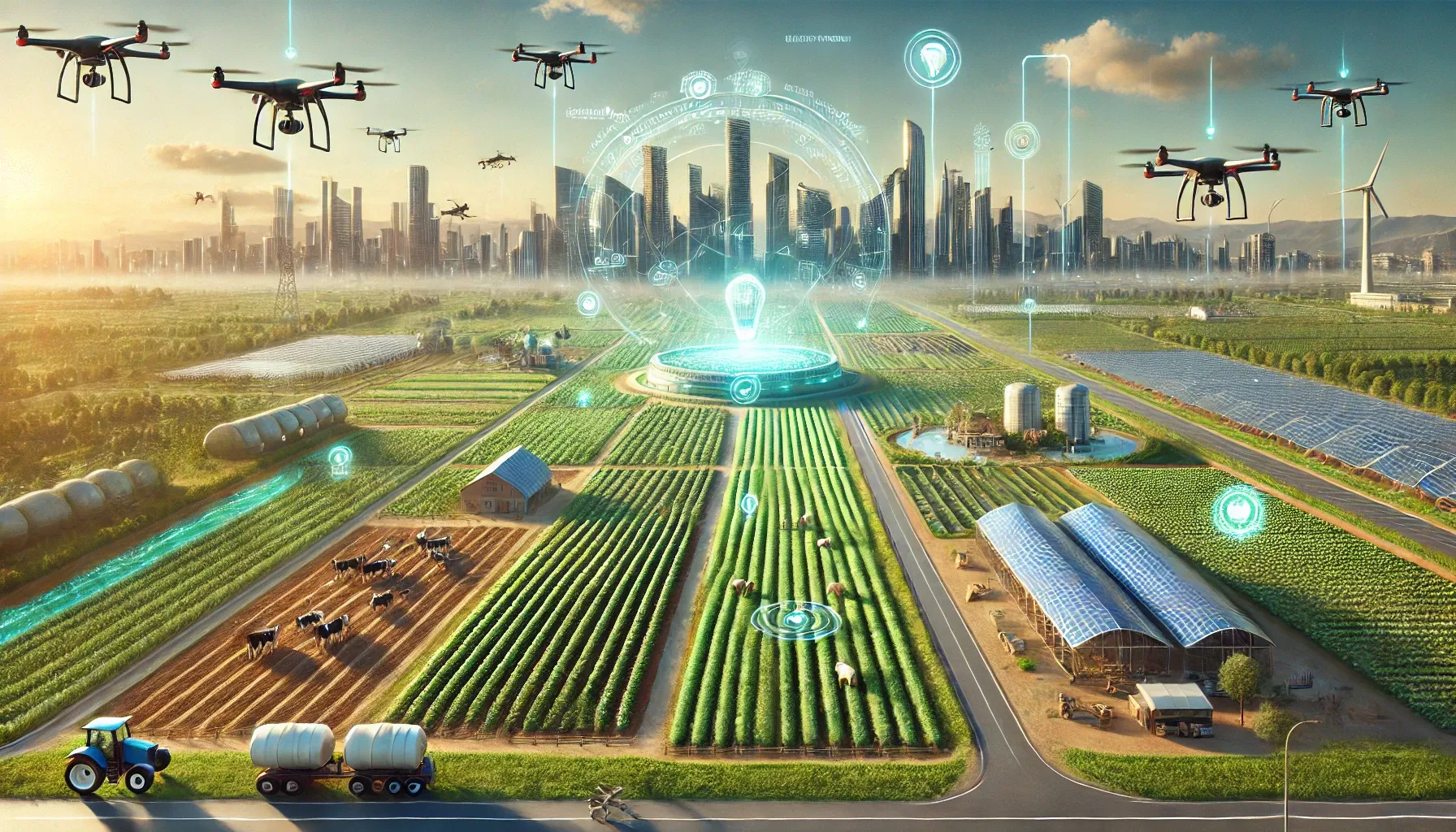
- Drones and IoT sensors to monitor soil health, weather conditions and crop growth.
- Automated irrigation systems that use artificial intelligence to optimize water use based on weather forecasts.
- Blockchain for product and livestock product traceability, ensuring food safety and security.
- Rotational grazing systems to ensure pasture recovery and prevent overgrazing.
- Organic food production and reduced reliance on chemical fertilizers to maintain soil health.
- Waste management systems that use livestock waste for the production of biogas and organic fertilizer.
- Farmers Markets and Agricultural Processing Hubs within AHNAKOT SMART CITY to ensure direct supply of fresh produce.
- Agritourism areas where visitors can experience the rural way of life and learn about sustainable agricultural practices.
- Green corridors that connect agricultural land with the urban area, enabling easy transport of goods and labor.
Agricultural Innovation Center to develop better crop varieties, improve agricultural techniques and encourage cooperation between universities and local farmers.
Livestock breeding programs to ensure the development of high quality breeds that can adapt to climate change.
Solar-powered irrigation systems and stables to reduce the carbon footprint of agricultural activities.
Biogas plants that use livestock waste to produce electricity for local communities.
-Rainwater harvesting systems throughout the agricultural land to optimize water use.
Aquaponic systems that combine fish farming and plant farming, using less water, and
The concept will be supported by Education Programs for local farmers on sustainable practices, along with a focus on increasing export potential for agricultural products. This approach would ensure food security for AHNAKOT SMART CITY while boosting the economic growth of the region.
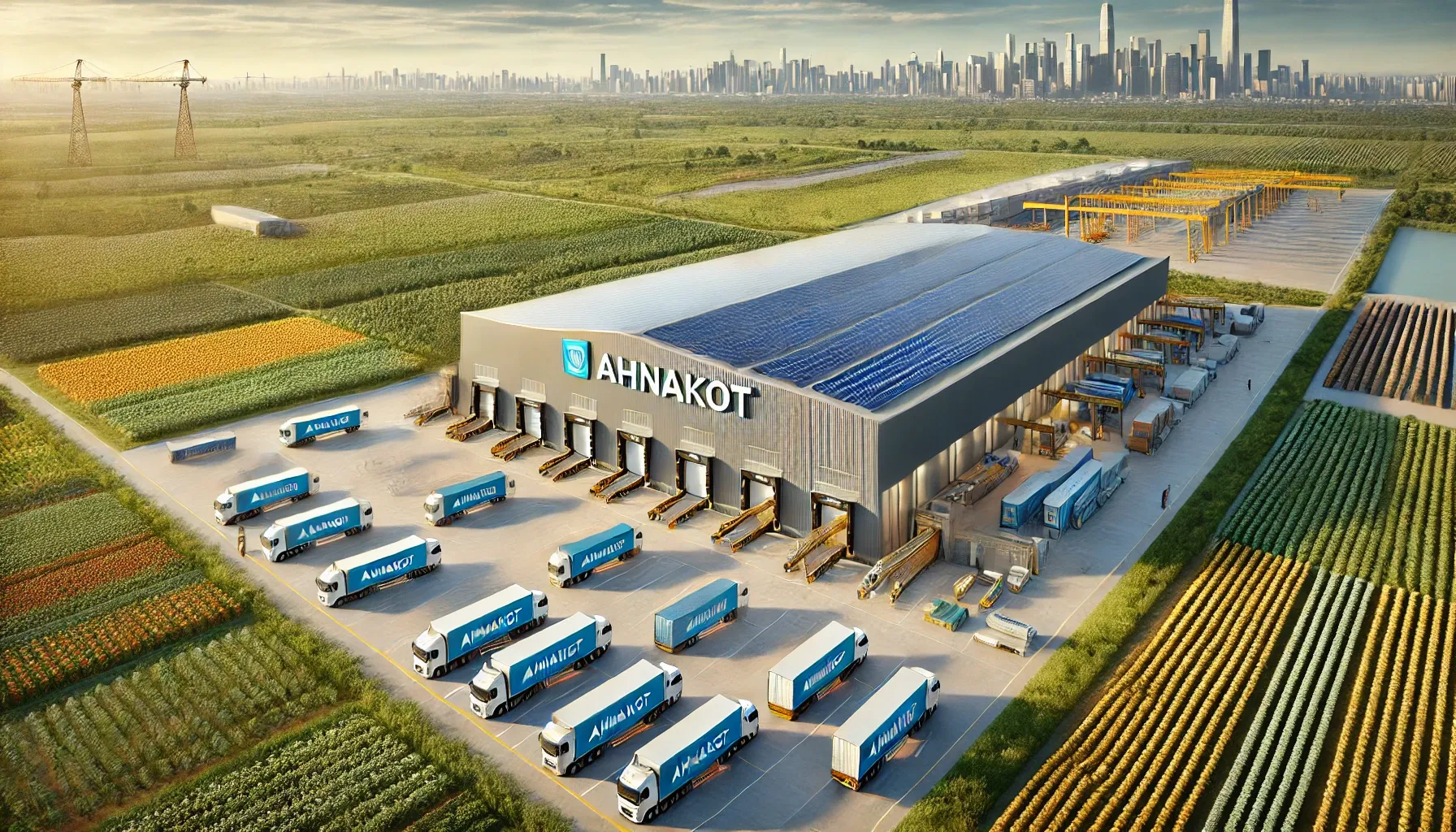
Warehouse Center
The AHNAKOT Warehouse Center for agricultural products can be designed with several key concepts in mind, focusing on efficiency, sustainability, and integration with advanced technologies. Below are the main concepts that could shape the warehouse and its operations:
Zoning for Product Categories: Separate zones for raw produce, processed agricultural goods, and export-ready items.
Automated Sorting Systems: Use of conveyor belts, robotic arms, and AI-driven sorting mechanisms to streamline the handling of products.
Modular Storage: Flexible storage units that can be adjusted to store varying volumes and types of goods, from grains to perishables.
Solar-Powered Facility: Rooftop solar panels to power the warehouse's lighting, machinery, and HVAC systems.
Energy-Efficient Lighting: LED systems with smart lighting controls to reduce energy consumption.
Waste Recycling Systems: Organic waste from spoiled or unsellable products is collected for composting or energy generation.
Real-Time Monitoring: IoT sensors for monitoring temperature, humidity, and stock levels to ensure product quality.
Automated Vehicles: Autonomous forklifts and loaders to move goods from storage to trucks.
Blockchain for Traceability: Blockchain technology to track the origin and quality of agricultural products, ensuring transparency in the supply chain.
AI-Driven Inventory Systems: Algorithms that predict demand, optimize stock levels, and manage reordering, ensuring the warehouse operates efficiently.
Temperature-Controlled Zones: Specific sections for perishable goods, equipped with smart refrigeration systems.
Automated Loading Docks: Sensors and automated systems ensure that the right products are loaded onto the right vehicles with minimal human intervention.
Seamless Connectivity to AHNAKOT Smart City Efficient transportation routes linking the warehouse to urban centers, ensuring quick distribution of goods.
Export-Focused Operations: Specific sections for handling agricultural exports, ensuring that produce meets international quality standards.
Large-Scale Fleet of Vehicles: A fleet of branded trucks with eco-friendly engines for transporting products across regions
Water Recycling Systems: Systems for recycling water used in cleaning produce or cooling machinery, reducing wastage.
Green Roofing: Integration of green roofs to reduce the facility's heat load, enhancing energy efficiency.
Low-Emission Vehicles: Electric and hybrid vehicles for in-city distribution, reducing the carbon footprint of logistics.
AHNAKOT Branding: Prominent placement of the AHNAKOT brand on trucks, walls, equipment, and storage units throughout the warehouse.
Smart Design: Sleek, modern architectural elements with eco-friendly materials that reflect the brand's commitment to sustainability.
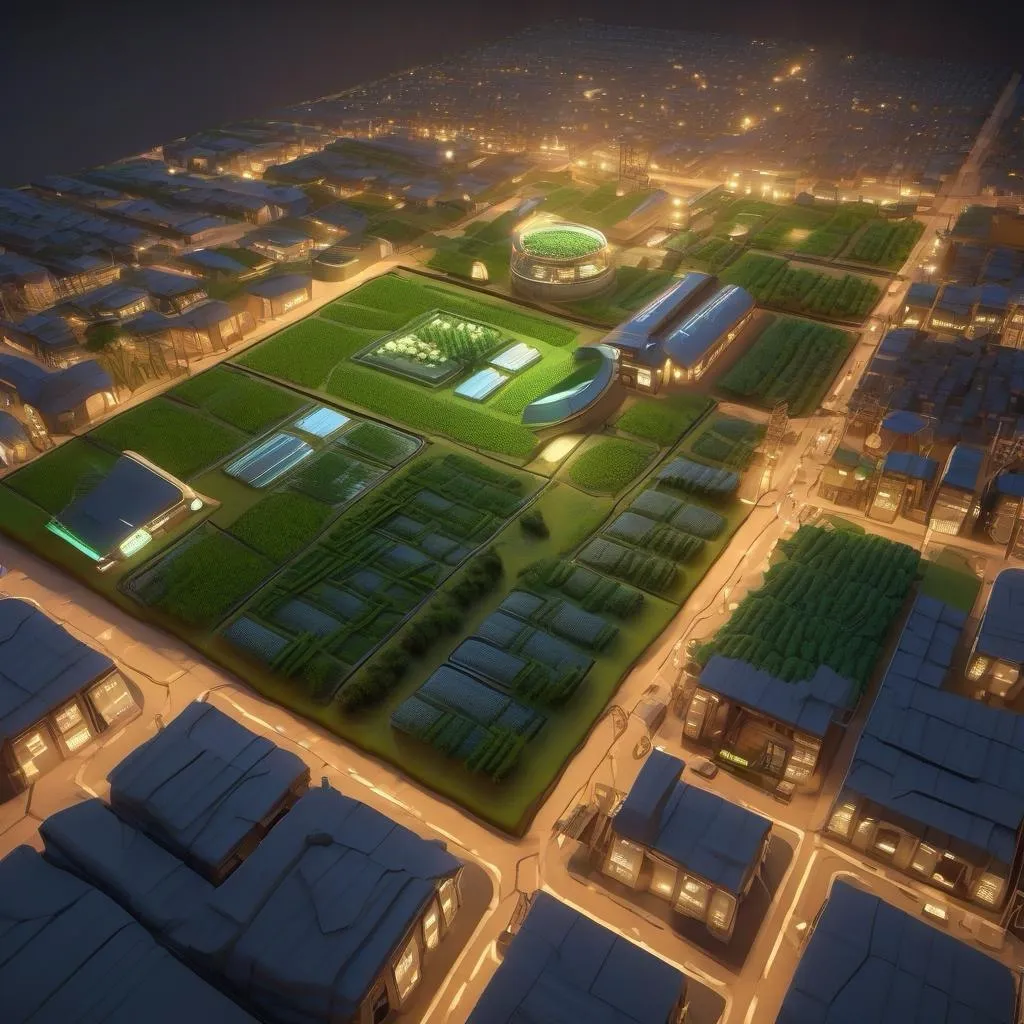

Agriculture and Livestock concept
The AHNAKOT Agriculture and Livestock concept on 40,000 hectares near AHNAKOT SMART CITY will integrate modern and sustainable agricultural practices, ensuring synergy between agriculture and urban development. Here are some key elements that will be included in this concept
- Visits: Different zones for rice, fruits and vegetables, designed for local consumption and export.
- Livestock: Dedicated areas for raising cattle, poultry and goats, with sustainable grazingpractices.
- Aquaculture: Ponds and irrigation tanks, which provide an additional source of food.
- Agroforestry: Combined agriculture with trees to promote biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Drones and IoT sensors to monitor soil health, weather conditions and crop growth.
- Automated irrigation systems that use artificial intelligence to optimize water use based on weather forecasts.
- Blockchain for product and livestock product traceability, ensuring food safety and security.
- Rotational grazing systems to ensure pasture recovery and prevent overgrazing.
- Organic food production and reduced reliance on chemical fertilizers to maintain soil health.
- Waste management systems that use livestock waste for the production of biogas and organic fertilizer.
- Farmers Markets and Agricultural Processing Hubs within AHNAKOT SMART CITY to ensure direct supply of fresh produce.
- Agritourism areas where visitors can experience the rural way of life and learn about sustainable agricultural practices.
- Green corridors that connect agricultural land with the urban area, enabling easy transport of goods and labor.
Agricultural Innovation Center to develop better crop varieties, improve agricultural techniques and encourage cooperation between universities and local farmers.
Livestock breeding programs to ensure the development of high quality breeds that can adapt to climate change.
Solar-powered irrigation systems and stables to reduce the carbon footprint of agricultural activities.
Biogas plants that use livestock waste to produce electricity for local communities.
-Rainwater harvesting systems throughout the agricultural land to optimize water use.
Aquaponic systems that combine fish farming and plant farming, using less water, and
The concept will be supported by Education Programs for local farmers on sustainable practices, along with a focus on increasing **export potential** for agricultural products. This approach would ensure food security for AHNAKOT SMART CITY while boosting the economic growth of the region.
AHNAKOT Warehouse Center
The AHNAKOT Warehouse Center for agricultural products can be designed with several key concepts in mind, focusing on efficiency, sustainability, and integration with advanced technologies. Below are the main concepts that could shape the warehouse and its operations:
Zoning for Product Categories: Separate zones for raw produce, processed agricultural goods, and export-ready items.
Automated Sorting Systems: Use of conveyor belts, robotic arms, and AI-driven sorting mechanisms to streamline the handling of products.
Modular Storage: Flexible storage units that can be adjusted to store varying volumes and types of goods, from grains to perishables.
Solar-Powered Facility: Rooftop solar panels to power the warehouse's lighting, machinery, and HVAC systems.
Energy-Efficient Lighting: LED systems with smart lighting controls to reduce energy consumption.
Waste Recycling Systems: Organic waste from spoiled or unsellable products is collected for composting or energy generation.
Real-Time Monitoring: IoT sensors for monitoring temperature, humidity, and stock levels to ensure product quality.
Automated Vehicles: Autonomous forklifts and loaders to move goods from storage to trucks.
Blockchain for Traceability: Blockchain technology to track the origin and quality of agricultural products, ensuring transparency in the supply chain.
AI-Driven Inventory Systems: Algorithms that predict demand, optimize stock levels, and manage reordering, ensuring the warehouse operates efficiently.
Temperature-Controlled Zones: Specific sections for perishable goods, equipped with smart refrigeration systems.
Automated Loading Docks: Sensors and automated systems ensure that the right products are loaded onto the right vehicles with minimal human intervention.
Seamless Connectivity to AHNAKOT Smart City Efficient transportation routes linking the warehouse to urban centers, ensuring quick distribution of goods.
Export-Focused Operations: Specific sections for handling agricultural exports, ensuring that produce meets international quality standards.
Large-Scale Fleet of Vehicles: A fleet of branded trucks with eco-friendly engines for transporting products across regions
Water Recycling Systems: Systems for recycling water used in cleaning produce or cooling machinery, reducing wastage.
Green Roofing: Integration of green roofs to reduce the facility's heat load, enhancing energy efficiency.
Low-Emission Vehicles: Electric and hybrid vehicles for in-city distribution, reducing the carbon footprint of logistics.
AHNAKOT Branding: Prominent placement of the AHNAKOT brand on trucks, walls, equipment, and storage units throughout the warehouse.
Smart Design: Sleek, modern architectural elements with eco-friendly materials that reflect the brand's commitment to sustainability.
Discover what’s possible with Understood
Project Portal Link
-
PROJECT SECTOR 1
- 1.Affordable Housing District
- 2.African Harbor District
- 3.Agricultural and Food Production District
- 4.Agriculture and Livestock District
- 5.AIRPORT
- 6.Arabic Harbor District
- 7. AREYATHOR KHMER District
- 8.Buddhism Park History
- 9.Cambodian Historical and Cultural Museum
- 10.CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT (CBD)
- 11.Christian Park History
- 12.City-Wide Integration and Features
- 13.Cultural and Arts District
- 14.Digital and Communications District
- 15.Education and Knowledge District
- 16.Entertainment and Media District
- 17.Environmental Education and Awareness District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 2
- 18.Environmental Research and Development District
- 19.Environmental Conservation District
- 20.Financial District
- 21.French Harbor District
- 22.Government and Administrative District
- 23.Greek Harbor District
- 24.Green Energy and Sustainability District
- 25.Health and Wellness District
- 26.HINDUISM PARK HISTORY
- 27.Historical and Heritage District
- 28.Innovation and Research District
- 29.Islamic History Park
- 31.Japanese Harbor District
- 32.Judaism Park History
- 33.Khmer Harbor District
- 34.Lake Tower District
- 35.Luxury Residential District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 3
- 36.MARINA DISTRICT
- 37.Mexican Harbor District
- 38.Museum Of The Future
- 39.Portuguese Harbor District
- 40.Public Services and Infrastructure District
- 41.Residential Districts
- 42.Retail and Commerce District
- 43.Smart Industrial and Manufacturing District
- 44.Smart Mobility and Transportation District
- 45.Smart Technology and AI District
- 46.Sports and Recreation District
- 47.Tech and Innovation District
- 48.Tourism and Hospitality District
- 49.Transport and Logistics District
- 50.Urban Agriculture and Food Security District V
- 51.Urban Design and Architecture District
- 52.Waterfront District
Project Portal Link
-
PROJECT SECTOR 1
- 1.Affordable Housing District
- 2.African Harbor District
- 3.Agricultural and Food Production District
- 4.Agriculture and Livestock District
- 5.AIRPORT
- 6.Arabic Harbor District
- 7. AREYATHOR KHMER District
- 8.Buddhism Park History
- 9.Cambodian Historical and Cultural Museum
- 10.CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT (CBD)
- 11.Christian Park History
- 12.City-Wide Integration and Features
- 13.Cultural and Arts District
- 14.Digital and Communications District
- 15.Education and Knowledge District
- 16.Entertainment and Media District
- 17.Environmental Education and Awareness District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 2
- 18.Environmental Research and Development District
- 19.Environmental Conservation District
- 20.Financial District
- 21.French Harbor District
- 22.Government and Administrative District
- 23.Greek Harbor District
- 24.Green Energy and Sustainability District
- 25.Health and Wellness District
- 26.HINDUISM PARK HISTORY
- 27.Historical and Heritage District
- 28.Innovation and Research District
- 29.Islamic History Park
- 31.Japanese Harbor District
- 32.Judaism Park History
- 33.Khmer Harbor District
- 34.Lake Tower District
- 35.Luxury Residential District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 3
- 36.MARINA DISTRICT
- 37.Mexican Harbor District
- 38.Museum Of The Future
- 39.Portuguese Harbor District
- 40.Public Services and Infrastructure District
- 41.Residential Districts
- 42.Retail and Commerce District
- 43.Smart Industrial and Manufacturing District
- 44.Smart Mobility and Transportation District
- 45.Smart Technology and AI District
- 46.Sports and Recreation District
- 47.Tech and Innovation District
- 48.Tourism and Hospitality District
- 49.Transport and Logistics District
- 50.Urban Agriculture and Food Security District V
- 51.Urban Design and Architecture District
- 52.Waterfront District