AHNAKOT
Green Energy and Sustainability District
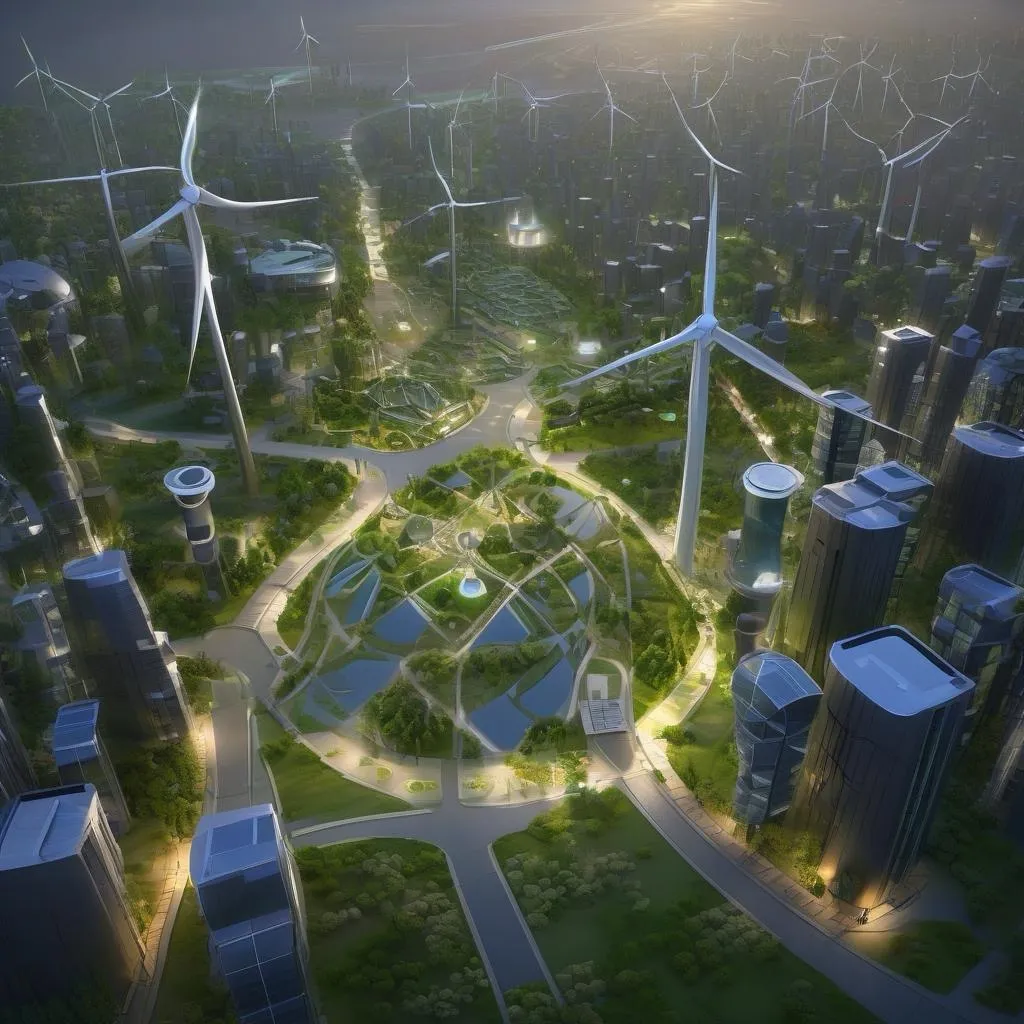
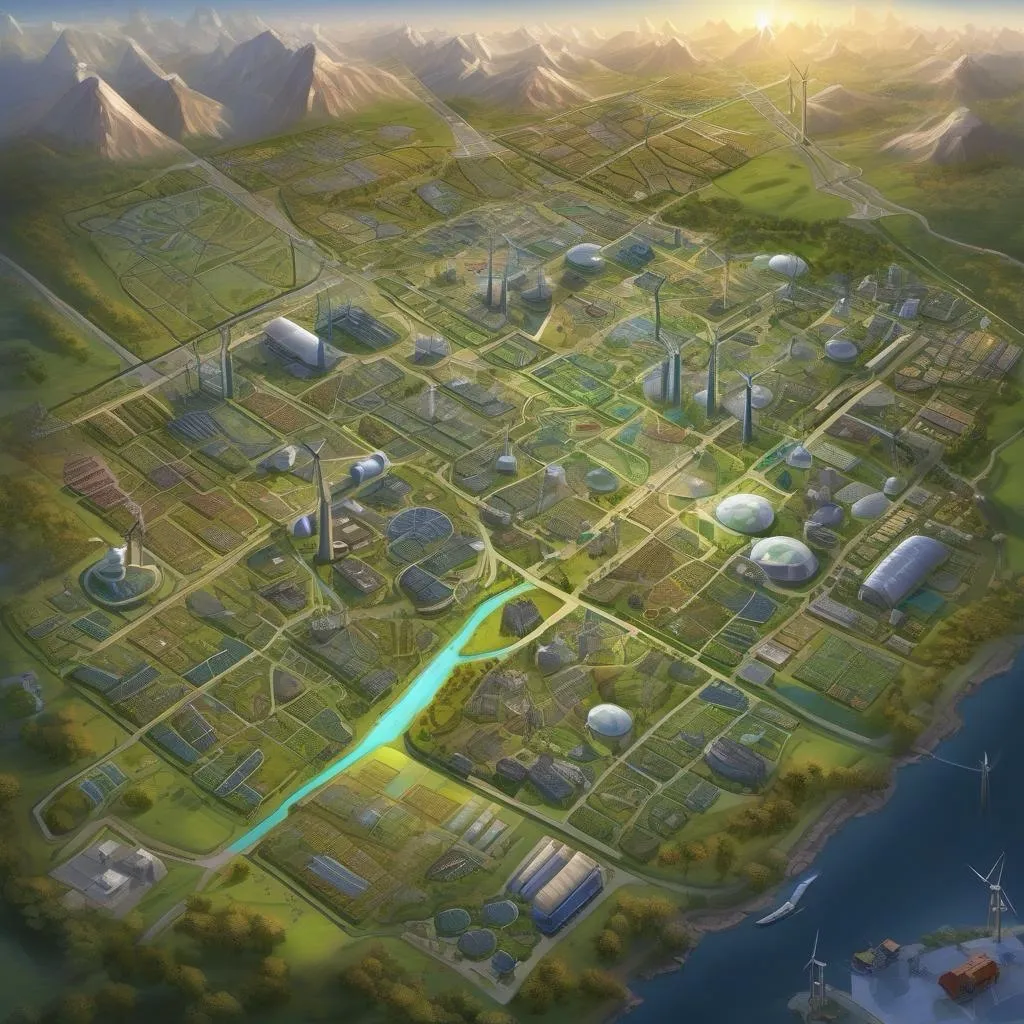
The AHNAKOT Green Energy and Sustainability District is envisioned as a pioneering urban area dedicated to sustainability, environmental stewardship, and renewable energy. This district serves as a model for sustainable urban development, integrating cutting-edge green technologies, ecofriendly infrastructure, and innovative practices that reduce carbon emissions, conserve resources, and promote a harmonious relationship with nature. The AHNAKOT Green Energy and Sustainability District is designed to be a living laboratory for green innovation, where residents, businesses, and visitors can experience the future of sustainable living.


Green Energy and Sustainability District
- Solar Power: The district is powered by a comprehensive network of solar panels installed on rooftops, solar farms, and even solar streets. These systems capture and convert sunlight into electricity, significantly reducing the district’s reliance on fossil fuels.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines, both large-scale and smaller urban models, are strategically placed throughout the district to harness wind energy. These turbines contribute to the district's energy grid, providing a consistent and renewable source of power.
- Smart Grids and Energy Storage: The district operates on a smart grid that optimizes energy distribution, balances supply and demand, and integrates renewable energy sources. Advanced energy storage systems, such as batteries and flywheels, store excess energy for use during peak demand or when renewable sources are not generating power.
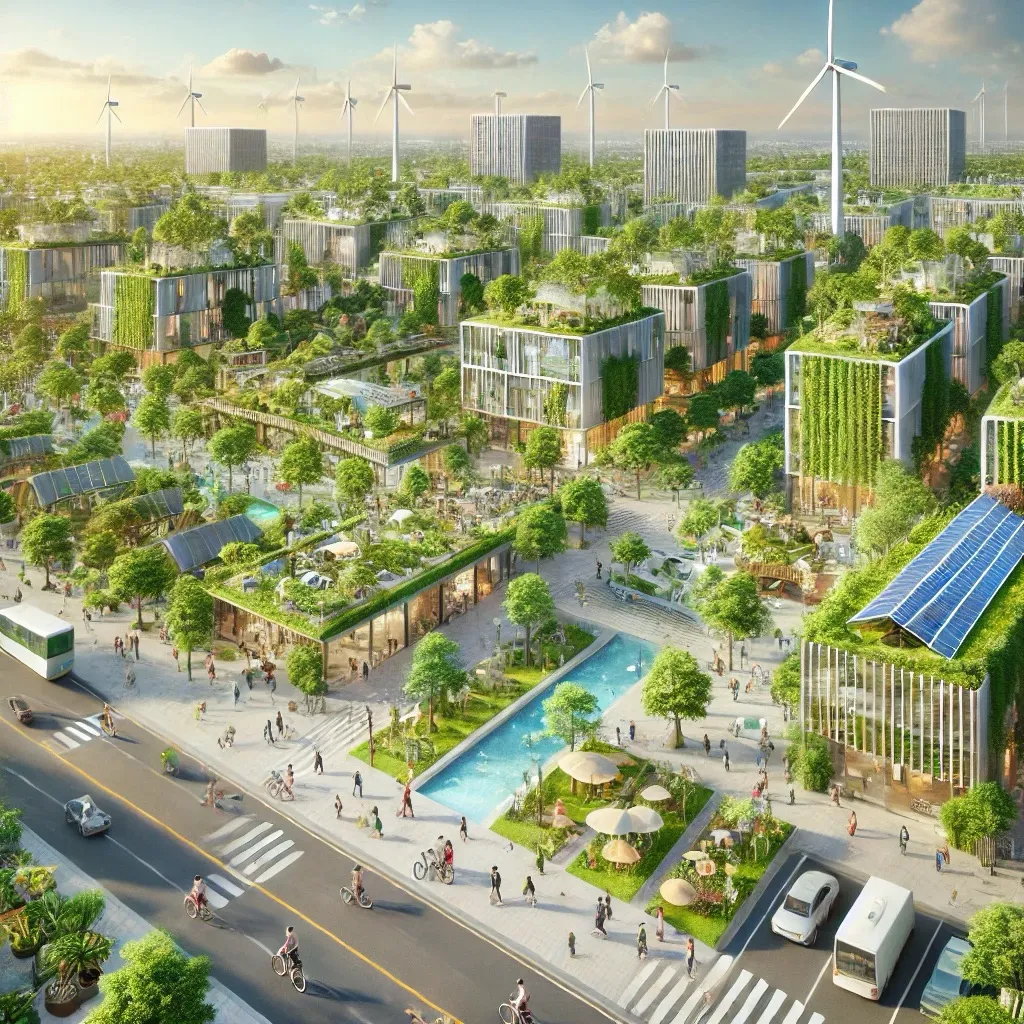
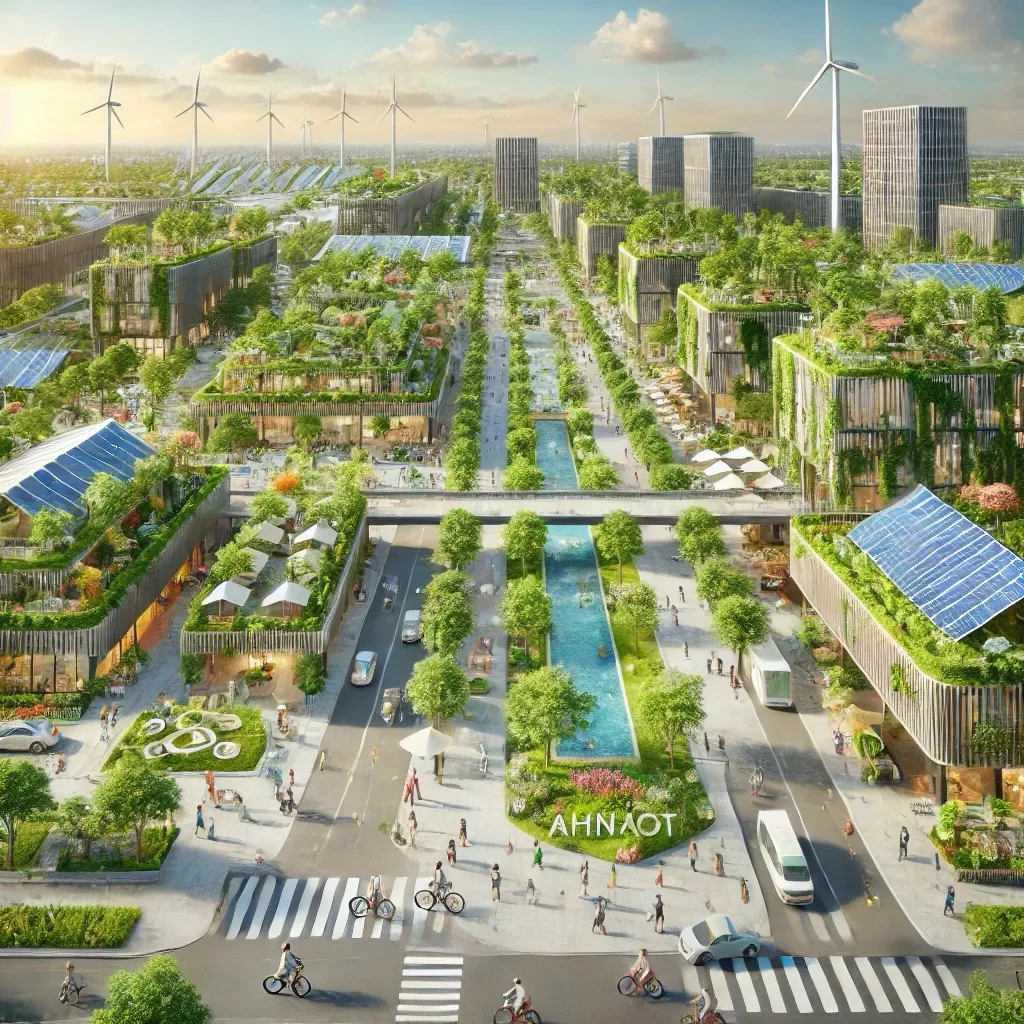
- Green Buildings: All buildings in the district are constructed using sustainable materials and designed to meet the highest standards of energy efficiency. Features include high-performance insulation, low-energy lighting, and energy-efficient HVAC systems.
- Passive Solar Design: Buildings are oriented and designed to maximize natural light and heat during the winter and minimize it during the summer. This reduces the need for artificial heating and cooling, lowering energy consumption.
- Green Roofs and Walls: Many buildings in the district feature green roofs and living walls, which help insulate buildings, reduce the urban heat island effect, and provide habitats for urban wildlife. These features also contribute to better air quality and aesthetic appeal.
- Rainwater Harvesting: The district is equipped with rainwater harvesting systems that collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and landscape maintenance. This reduces the demand on municipal water supplies and promotes water conservation.
- Greywater Recycling: Greywater recycling systems treat and reuse wastewater from sinks, showers, and washing machines for irrigation and other non-potable applications. This reduces water waste and supports sustainable water management.
- Stormwater Management: The district incorporates green infrastructure, such as permeable pavements, bioswales, and constructed wetlands, to manage stormwater naturally. These systems prevent flooding, reduce runoff, and filter pollutants from rainwater before it reaches natural water bodies.
- Electric and Autonomous Vehicles: The district promotes the use of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous transportation. EV charging stations are widely available, and autonomous shuttles provide convenient, low-carbon public transportation.
- Bike and Pedestrian-Friendly Design: The district is designed to encourage walking and cycling, with extensive networks of bike lanes, pedestrian paths, and car-free zones. Bike-sharing programs and e-scooters are also available, promoting sustainable mobility.
- Public Transit Integration: The district is seamlessly connected to the city's public transportation network, with electric buses, trams, and trains providing efficient and environmentally friendly transit options for residents and visitors.
- Zero-Waste Initiatives: The district operates under a zero-waste philosophy, with comprehensive recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy programs. Residents and businesses are encouraged to reduce, reuse, and recycle, minimizing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
- Circular Economy Practices: The district supports a circular economy by promoting the reuse and recycling of materials, reducing resource extraction, and encouraging the design of products with a longer lifecycle. Businesses and manufacturers are encouraged to adopt sustainable practices that minimize waste and environmental impact.
- Urban Agriculture and Composting: Community gardens, rooftop farms, and vertical agriculture are integral parts of the district, providing fresh, locally grown produce. Organic waste is composted and used to enrich the soil, closing the loop in the food system.
- Sustainable Living Education: The district offers education and outreach programs on sustainable living, including workshops, seminars, and community events. Residents and visitors are encouraged to adopt eco-friendly practices in their daily lives.
- Green Spaces and Recreation: The district is designed with abundant green spaces, including parks, community gardens, and nature reserves. These areas provide opportunities for recreation, relaxation, and connection with nature, enhancing the quality of life for residents.
- Eco-Friendly Retail and Dining: Local businesses in the district are encouraged to adopt sustainable practices, offering products and services that prioritize environmental responsibility. Restaurants and cafes focus on locally sourced, organic, and plant-based foods, reducing the district’s carbon footprint.
- Green Technology Incubators: The district hosts incubators and innovation hubs that support the development of green technologies, such as renewable energy solutions, sustainable materials, and eco-friendly products. These incubators provide startups with the resources and networks needed to bring their innovations to market.
- Research Institutes: The district includes research institutes dedicated to studying environmental science, climate change, and sustainable urban development. These institutes collaborate with universities, government agencies, and private companies to advance knowledge and develop new solutions to environmental challenges.
- Living Labs: The district serves as a living lab for sustainability, where new technologies and practices can be tested and refined in a real-world setting. This approach allows for continuous improvement and adaptation of sustainable practices.
Vision for the AHNAKOT Green Energy and Sustainability District
The AHNAKOT Green Energy and Sustainability District is designed to be a beacon of environmental innovation and sustainable living. By integrating renewable energy, sustainable architecture, and green infrastructure, the district aims to minimize its environmental impact while providing a high quality of life for its residents. The district’s focus on community engagement, education, and innovation ensures that it remains a dynamic and inspiring model for sustainable urban development.
Project Portal Link
-
PROJECT SECTOR 1
- 1.Affordable Housing District
- 2.African Harbor District
- 3.Agricultural and Food Production District
- 4.Agriculture and Livestock District
- 5.AIRPORT
- 6.Arabic Harbor District
- 7. AREYATHOR KHMER District
- 8.Buddhism Park History
- 9.Cambodian Historical and Cultural Museum
- 10.CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT (CBD)
- 11.Christian Park History
- 12.City-Wide Integration and Features
- 13.Cultural and Arts District
- 14.Digital and Communications District
- 15.Education and Knowledge District
- 16.Entertainment and Media District
- 17.Environmental Education and Awareness District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 2
- 18.Environmental Research and Development District
- 19.Environmental Conservation District
- 20.Financial District
- 21.French Harbor District
- 22.Government and Administrative District
- 23.Greek Harbor District
- 24.Green Energy and Sustainability District
- 25.Health and Wellness District
- 26.HINDUISM PARK HISTORY
- 27.Historical and Heritage District
- 28.Innovation and Research District
- 29.Islamic History Park
- 31.Japanese Harbor District
- 32.Judaism Park History
- 33.Khmer Harbor District
- 34.Lake Tower District
- 35.Luxury Residential District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 3
- 36.MARINA DISTRICT
- 37.Mexican Harbor District
- 38.Museum Of The Future
- 39.Portuguese Harbor District
- 40.Public Services and Infrastructure District
- 41.Residential Districts
- 42.Retail and Commerce District
- 43.Smart Industrial and Manufacturing District
- 44.Smart Mobility and Transportation District
- 45.Smart Technology and AI District
- 46.Sports and Recreation District
- 47.Tech and Innovation District
- 48.Tourism and Hospitality District
- 49.Transport and Logistics District
- 50.Urban Agriculture and Food Security District V
- 51.Urban Design and Architecture District
- 52.Waterfront District
Project Portal Link
-
PROJECT SECTOR 1
- 1.Affordable Housing District
- 2.African Harbor District
- 3.Agricultural and Food Production District
- 4.Agriculture and Livestock District
- 5.AIRPORT
- 6.Arabic Harbor District
- 7. AREYATHOR KHMER District
- 8.Buddhism Park History
- 9.Cambodian Historical and Cultural Museum
- 10.CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT (CBD)
- 11.Christian Park History
- 12.City-Wide Integration and Features
- 13.Cultural and Arts District
- 14.Digital and Communications District
- 15.Education and Knowledge District
- 16.Entertainment and Media District
- 17.Environmental Education and Awareness District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 2
- 18.Environmental Research and Development District
- 19.Environmental Conservation District
- 20.Financial District
- 21.French Harbor District
- 22.Government and Administrative District
- 23.Greek Harbor District
- 24.Green Energy and Sustainability District
- 25.Health and Wellness District
- 26.HINDUISM PARK HISTORY
- 27.Historical and Heritage District
- 28.Innovation and Research District
- 29.Islamic History Park
- 31.Japanese Harbor District
- 32.Judaism Park History
- 33.Khmer Harbor District
- 34.Lake Tower District
- 35.Luxury Residential District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 3
- 36.MARINA DISTRICT
- 37.Mexican Harbor District
- 38.Museum Of The Future
- 39.Portuguese Harbor District
- 40.Public Services and Infrastructure District
- 41.Residential Districts
- 42.Retail and Commerce District
- 43.Smart Industrial and Manufacturing District
- 44.Smart Mobility and Transportation District
- 45.Smart Technology and AI District
- 46.Sports and Recreation District
- 47.Tech and Innovation District
- 48.Tourism and Hospitality District
- 49.Transport and Logistics District
- 50.Urban Agriculture and Food Security District V
- 51.Urban Design and Architecture District
- 52.Waterfront District
Contact us
Discover what’s possible with Understood
Project Portal Link
-
PROJECT SECTOR 1
- 1.Affordable Housing District
- 2.African Harbor District
- 3.Agricultural and Food Production District
- 4.Agriculture and Livestock District
- 5.AIRPORT
- 6.Arabic Harbor District
- 7. AREYATHOR KHMER District
- 8.Buddhism Park History
- 9.Cambodian Historical and Cultural Museum
- 10.CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT (CBD)
- 11.Christian Park History
- 12.City-Wide Integration and Features
- 13.Cultural and Arts District
- 14.Digital and Communications District
- 15.Education and Knowledge District
- 16.Entertainment and Media District
- 17.Environmental Education and Awareness District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 2
- 18.Environmental Research and Development District
- 19.Environmental Conservation District
- 20.Financial District
- 21.French Harbor District
- 22.Government and Administrative District
- 23.Greek Harbor District
- 24.Green Energy and Sustainability District
- 25.Health and Wellness District
- 26.HINDUISM PARK HISTORY
- 27.Historical and Heritage District
- 28.Innovation and Research District
- 29.Islamic History Park
- 31.Japanese Harbor District
- 32.Judaism Park History
- 33.Khmer Harbor District
- 34.Lake Tower District
- 35.Luxury Residential District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 3
- 36.MARINA DISTRICT
- 37.Mexican Harbor District
- 38.Museum Of The Future
- 39.Portuguese Harbor District
- 40.Public Services and Infrastructure District
- 41.Residential Districts
- 42.Retail and Commerce District
- 43.Smart Industrial and Manufacturing District
- 44.Smart Mobility and Transportation District
- 45.Smart Technology and AI District
- 46.Sports and Recreation District
- 47.Tech and Innovation District
- 48.Tourism and Hospitality District
- 49.Transport and Logistics District
- 50.Urban Agriculture and Food Security District V
- 51.Urban Design and Architecture District
- 52.Waterfront District
Project Portal Link
-
PROJECT SECTOR 1
- 1.Affordable Housing District
- 2.African Harbor District
- 3.Agricultural and Food Production District
- 4.Agriculture and Livestock District
- 5.AIRPORT
- 6.Arabic Harbor District
- 7. AREYATHOR KHMER District
- 8.Buddhism Park History
- 9.Cambodian Historical and Cultural Museum
- 10.CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT (CBD)
- 11.Christian Park History
- 12.City-Wide Integration and Features
- 13.Cultural and Arts District
- 14.Digital and Communications District
- 15.Education and Knowledge District
- 16.Entertainment and Media District
- 17.Environmental Education and Awareness District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 2
- 18.Environmental Research and Development District
- 19.Environmental Conservation District
- 20.Financial District
- 21.French Harbor District
- 22.Government and Administrative District
- 23.Greek Harbor District
- 24.Green Energy and Sustainability District
- 25.Health and Wellness District
- 26.HINDUISM PARK HISTORY
- 27.Historical and Heritage District
- 28.Innovation and Research District
- 29.Islamic History Park
- 31.Japanese Harbor District
- 32.Judaism Park History
- 33.Khmer Harbor District
- 34.Lake Tower District
- 35.Luxury Residential District
-
PROJECT SECTOR 3
- 36.MARINA DISTRICT
- 37.Mexican Harbor District
- 38.Museum Of The Future
- 39.Portuguese Harbor District
- 40.Public Services and Infrastructure District
- 41.Residential Districts
- 42.Retail and Commerce District
- 43.Smart Industrial and Manufacturing District
- 44.Smart Mobility and Transportation District
- 45.Smart Technology and AI District
- 46.Sports and Recreation District
- 47.Tech and Innovation District
- 48.Tourism and Hospitality District
- 49.Transport and Logistics District
- 50.Urban Agriculture and Food Security District V
- 51.Urban Design and Architecture District
- 52.Waterfront District